- [PART 1 of 2] Billy is a 16 year old male that jokingly takes his girlfriend’s pregnancy which subsequently turns positive. He thought this was rather unusual, so he decides to get checked out by his primary care physician. He is also experiencing gynecomastia. If the physician finds a testicular tumor, which of the following is most likely?
- Seminoma
- Yolk sac tumor
- Choriocarcinoma
- Teratoma
- Leydig cell tumor Answer C. Choriocarcinoma is classically associated with an increase in hCG (indicated by the positive pregnancy test). It is also associated with gynecomastia and hyperthyroidism. This is because hCG shares the α-subunit with TSH, FSH, and LH.
Inflammatory and neoplastic disorders of the prostate and testes.
Inflammatory and neoplastic disorders of the prostate and testes.
- [PART 2 of 2] Billy is a 16 year old male that jokingly takes his girlfriend’s pregnancy which subsequently turns positive. He thought this was rather unusual, so he decides to get checked out by his primary care physician. He is also experiencing gynecomastia. If the physician finds a testicular tumor, which of the following would most likely be found on histology?
- Distorted Syncytiotrophoblasts
- Psammoma bodies
- Schiller-Duval Bodies
- Call-Exner bodies
- Necrosis Answer A. Choriocarcinoma would show distorted syncytiotrophoblasts and cytotrophoblasts on histology.
Inflammatory and neoplastic disorders of the prostate and testes.
- A 4 year old male presents with a non-tender testicular mass. Labs show an increase in α-fetal protein. Which of the following would most likely bee seen on biopsy?
- Psammoma bodies
- Call Exner Bodies
- Reinke crystals
- Schiller-Duval Bodies
- Coffee bean nuclei Answer D. Due to this patients age and presence of AFP, this patient most likely has a Yolk Sac Tumor.
Inflammatory and neoplastic disorders of the prostate and testes.
- A 67 year old female presents with abdominal pain for the last month. Last menstrual period was 10 years prior. Physical examination reveals a left adnexal mass and an ovarian biopsy is ordered. Histology shows proliferative, jagged lining with psammoma bodies. Which of the following would also be present in this patient and be most helpful in confirming the diagnosis?
- hCG
- α-fetoprotein
- Excess E2
- CA-125
- AFP Answer D. Diagnosis is cystadenocarcinoma due to the description of “jagged lining” and presence of psammoma bodies. CA-125 is a unique serum marker for cystadenocarcinoma.
Neoplastic lesions of ovaries and uterus.
- A 67 year old female presents with ascites and pleural effusion. She also has a pelvic mass. She is diagnosed with Meigs syndrome. Which of the following types of tumors is most likely to be identified in this patient?
- Yolk sac carcinoma
- Choriocarcinoma
- Leydig Carcinoma
- Seminoma
- FibromaAnswer E. Meigs syndrome is often associated with ovarian fibromas. Know Meigs triad: Fibroma, ascites, and pleural effusion.
Neoplastic lesions of ovaries and uterus.
- Which of the following tumors is associated with Reinke crystals?
- Sertoli Tumor
- Leydig Tumor
- Choriocarcinoma
- Dysgerminoma
- Teratoma Answer B. Remember that you dig for crystals (LeyDIG).
Neoplastic lesions of ovaries and uterus.
- An ovarian tumor is biopsied and pathology identifies mucin secreting cells with signet ring morphology. You diagnose it as a krukenberg tumor. Which of the following is the most likely location of the primary tumor?
- Ovary
- Bone
- GI
- Lung
- Cervix Answer C. Kruckenberg tumors are metastatic growth from the GI and breast.
Neoplastic lesions of ovaries and uterus.
- A 32 year old female presents with bloody nipple discharge. A biopsy is performed. Which of the following is most likely to be found by the path lab?
- Well developed fibrovascular stalks and supported by myoepithelial cells
- A lack of myoepithelial cells
- Hypercellular stroma with leaf-like formation
- Cheesy necrotic material
- Mucin secretion with signet ring formation Answer A. The most common cause of bloody nipple discharge is intraductal papilloma which is consistent with the description of answer A.
Breast Neoplasms.
- [PART 1 of 2] A 36 year old female patient presents to her OB-GYN with an erythematous, scaly red rash around her right nipple. Onset was approximately 2 weeks prior and patient was put on dicloxacillin by her PCP but doesn’t seem to help. Patient is 2 months postpartum and is currently breastfeeding. Breast is non-tender and is negative for edema. Patient vitals are within range and is afebrile. Which of the following is the most appropriate course of action?
- Perform an ultrasound-guided aspiration
- Order a mammogram
- Switch to Vancomycin
- Switch to TMP-SMX
- Advise patient to stop breastfeeding on affected breastAnswer B.
Breast Neoplasms.
- [PART 2 of 2] What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Ductal cell carcinoma in situ
- Lobular cell carcinoma in situ
- Inflammatory breast carcinoma
- Acute mastitis
- Chronic mastitis Answer A. Despite this patients risk factor (breast-feeding) for acute mastitis, this patient’s breast is “non-tender” and lesion is described as “scaly.” This suggests Paget’s Disease of the nipple, which is a common comorbidity of Ductal cell carcinoma in situ. Inflammatory breast carcinoma should also be considered, but usually would present with symptoms more similar to mastitis (erythema, edema) and would lack the “scaly” description.
Breast Neoplasms.
- A 26 year old male patient presents to the clinic with symptoms of inflammatory arthritis and conjunctivitis, and urethritis. Patient admits to having unprotected sex which prompts you to do further testing for STIs. Based on the symptomology, what is the most likely antibiotic combination you will use to combat the patients STI?
- Penicillin + Ceftriazone
- Cefriaxone + Azithromycin
- Azithromycin + Penicillin
- Penicillin alone
- Azithromycin alone Answer B. This patient is displaying symptoms of Reiter’s syndrome which is most likely caused by Chlamydia. However, coinfections with gonorrhea are so common that you should always treat for both (in real life, and ALWAYS on boards). Azithromycin treats chlamydia while ceftriaxone treats gonorrhea. Gonorrhea can also cause Reiter’s but less often.
STIs.
- You are trying to identify an unknown bacterium. It grows on chocolate agar and New York City Agar. It is positive for fermentation of glucose and maltose. Which of the following is most likely the identity of this bacterium?
- Chlamydia trachomatis
- Treponema pallidum
- Gardnerella vaginalis
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Neisseria meningitidisAnswer E.
STIs.
- Which of the following is NOT true regarding trichomonas vaginalis?
- It is usually asymptomatic, but can cause cervical petechiae when symptomatic
- It uses hydrogenosome which allows it to produce ATP without the presence of O2
- Decreased vaginal pH is a defining symptom
- NAAT is the preferred method of diagnosis
- IT will have a characteristic jerking/spinning motility on wet mount microscopy Answer C. Increased vaginal pH is a defining symptom.
STIs.
- [PART 1 of 2] A 32 year old female presents with a pruritic maculopapular rash on the palms, soles and torso. She admits to having unprotected sex and you run a multitide of tests for various STIs. The tests come back positive for syphilis, as you expected. However, the patient is allergic to penicillin. What is the most appropriate course of treatment?
- Azithromycin
- Doxycycline
- Desensitize patient and utilize penicillin
- Ceftriaxone
- Pipercillin Answer C. It is always best to desensitize patient because alternative drugs (doxycycline) are suboptimal.
STIs.
- [PART 2 of 2] Which of the following tests would need to be positive to allow for a diagnosis of syphilis?
- RPR only
- TPPA and FTA-ABS
- VDRL and RPR
- RPR and TPPA
- FTA-ABS and MHA-TPAnswer D. A diagnosis of syphilis requires both a non-treponemal test (RPR, VDRL) and a treponemal test (FTA-ABS, TPPA, MHA-TP) to be positive. This is because non-treponemal tests have a high rate of false-positives.
STIs.
- Which of the following is characteristic for Haemophilus ducreyi infections?
- Railroad track appearance on gram stain
- Clue cells on wet mount microscopy
- Strawberry cervix
- Painless ulcers
- Donovan bodies Answer A.
STIs.
- Urinary canaliculi are often associated with which of the following STIs?
- Syphilis
- Mycoplasma
- Haemophilus ducreyi
- Klebsiella granulomatis
- Ureaplasma Answer E.
STIs.
- Which of the following is a viral pathogen that utilizes reverse transcriptase but is NOT a retrovirus?
- HIV-1
- HTLV-1
- HBV
- HCV
- HTLV-2Answer C.
HIV.
- Which of the following is associated with Adult T-cell Leukemia (ATL)?
- HTLV-1
- HTLV-2
- HIV-1
- HIV-2
- HPVAnswer A. ATL occurs in 2-5% of those infected with HTLV-1.
- Which of the following would distinguish bacillary angiomatosis from kaposi sarcoma?
- HHV-8 infection
- Patient has HIV
- Skin lesions
- Mixed infiltrate
- AngioproliferationAnswer D.
- A 24 year old, male patient presents with a headache, sore throat, fatigue and fever that began 2 weeks prior. The patient has a history of IV drug abuse and labs show drastically decreased CD4+ cells. Which of the following describes the virus responsible for this patient’s presentation?
- Single-stranded DNA
- Double-stranded DNA
- Single-stranded RNA
- Double-stranded RNAAnswer C. HIV is a single-stranded RNA virus. It is also said to be diploid because in carries two copies of standard RNA.
- Drug compliance is extremely important in HIV+ patients due to the potential for drug resistance. Mutations in which of the following genes leads to HIV drug resistance?
- gag
- pol
- env
- CCR5
- CXC4Answer B. The pol gene codes for reverse transcriptase, integrase and protease which are the targets of HIV drugs. Gag codes for p24 (ELISA target) and env codes for gp160 (cell entry).
HIV.
- What is the drug of choice in treating HIV+ patients with disseminated MAC?
- Azithromycin
- Clarithromycin
- Tobramycin
- Neomycin
- TMP-SMXAnswer A.
HIV.
- One of your long-time patients, a 35 year-old male patient who is HIV+ presents to the clinic for a routine checkup. The patient has been overall well managed until recently when his CD4+ counts plummeted to less than 200. Additionally, he is recovering from a pneumocystis pneumonia for which the hospitalist prescribed TMP-SMX. While he has been able to fight the infection caused by PJP, you have concerns about the antibiotics prescribed resulting in which of the following problems?
- Acute kidney injury
- Liver failure
- Myocardial infarction
- Mitochondrial Toxicity
- Osteoporosis Answer A.
STIs and AIDs.
- Which of the following tests need to be performed if a provider plans to prescribe Maraviroc to a HIV+ patient?
- HLA-B*5701 Test
- Tropism Test
- Heterophile Antibody Monotest
- CBCAnswer B.
STIs and AIDs.
- [PART 1 of 2] Which of the following drugs is used during pregnancy to decrease the risk of fetal transmission in an HIV+ mother?
- Abacavir
- Tenofovir
- Efavirenz
- Zidovudine
- Nevirapine Answer D.
Pharmacology for HIV.
- [PART 2 of 2] Which of the following is a side effect from taking this medication?
- Mitochondrial Toxicity
- Nephrotoxicity
- Bone Marrow Suppression
- Hyperpigmentation
- RashAnswer C.
Pharmacology for HIV.
- Which of the following combinations of drugs would be most appropriate to treat an HIV+ patient?
- Tenofovir, Didanosine, and Efavirenz
- Stavudine, Didanosine, and Darunavir
- Abacavir, Zidovudine, and Atazanavir
- Abacavir, Zidovudine, and Stavudine
- Stavudine, Zidovudine, and Ritonavir Answer C. HAART therapy consists of two NRTIs plus one PI, NNRTI, or Integrase inhibitor. Drugs of the same nucleoside type should not be used in combination. Stavudine and Didanosine should not be used in combination due to having the same detrimental side effects.
Pharmacology for HIV.
- A 25 year old male patient presents to the clinic for a wellness exam. He is HIV+, but has been well controlled until recently. His viral load has been steadily increasing for the last 2 months and you are beginning to worry that this isn’t just a blip. The patient states that he has been compliant with his medications. He is also complaining of acid reflux for which he has been controlling with over-the-counter Prilosec (Omeprazole). Which of the following HAART medications is most likely being affected resulting in the increase in viral load?
- Atazanavir
- Etravirdine
- Didanosine
- Enfuvirtide
- Lopinavir Answer A. Atazanavir is contraindicated with antacids and proton pump inhibitors.
Pharmacology for HIV.
- A 32 year old female patient presents to the ER with symptoms of severe hypoxemia. The patient has a history of IV drug abuse. Labs show elevated LDH and CXR reveals diffuse, bilateral symmetrical ground glass interstitial infiltrates emanating from the hila in a butterfly pattern. Which of the following is the most appropriate immediate course of treatment?
- High dose TMP-SMX
- High dose fluconazole
- Begin HAART
- A & B
- B & CAnswer A. This patient is most likely HIV+ and suffering from pneumocystis pneumonia. High LDH, a “ground glass” appearance on CXR, and history of IV drug use should have let you to the diagnosis of PJP. PJP is treated with high-dose TMP-SMX. HAART therapy should not be started until 2 weeks following the onset of treatment of the PJP to minimize the risk for IRIS. Don’t forget that a spontaneous pneumothorax in a HIV+ patient should prompt consideration for PJP. Diagnosis of PJP includes GMS, DFA stain, PCR and Beta-D-Glucan tests.
AIDs and opportunistic infections.
- You are on rotations in the ICU when you come across a 45 year old male patient being treated for pneumocystis pneumonia. The attending has chosen to treat the patient with IV Pentamidine due to a sensitivity to TMP-SMX (the usual drug of choice). Your are monitoring the patient during the infusion when he becomes unresponsive. After notifying your attending, which of the following would be the most appropriate next step?
- Stop the infusion
- Check BGL
- Stop any HAART therapy
- Administer Insulin
- Perform vagal maneuverAnswer B. IV Pentamidine causes symptoms of hypoglycemia (especially during infusion), pancreatitis, AKI/Azotemia, and hypotension. Patients can sometimes become unresponsive during treatment due to hypoglycemia. Patients receiving this drug should be well hydrated to avoid AKI.
AIDs and opportunistic infections.
- You are on rotations in the ICU when you come across a 42 year old male patient being treated for a disseminated Cryptococcus infection. The patient was recently diagnosed with HIV and initially presented with a headache and stiff neck. He has not yet been started on HAART. The patient was put on IV Amphotericin B + oral 5-Flucytosine to combat the infection. Currently, the patient’s opening pressure is 30 mm H2. The patient is experiencing mild confusion, blurred vision, and papilledema. Which of the following would be an additional treatment you could recommend in order to assist with the patient’s symptoms?
- Start HAART
- Change to high dose Fluconazole
- Daily lumbar punctures
- Drill burr holes
- Administer high dose steroids Answer C. The patient is displaying symptoms of elevated intracranial pressure and has a CSF opening pressure of >25 mm H2. For these patients, it is recommended to perform daily lumbar punctures to help relieve this pressure. Recall that IV Amp B + 5-FC is the treatment of choice. Amp B is often replaced with high dose fluconazole when the symptoms are under control. Also, know that Cryptococcus is highly associated with IRIS so the provider should wait to administer HAART for at least 2 weeks following the onset of treatment for this infection.
AIDs and opportunistic infections.
- A 38 year old female patient who is HIV+ presents to the Emergency Department with headache, confusion, fever, and motor weakness. CD4+ counts are <200 and CT shows ring-enhancing lesions in the frontal and parietal lobes. The nurse notes that the patient lives alone and keeps asking for someone to check on her three cats while she is hospitalized. Which of the following is most likely responsible for her symptoms?
- Primary CNS lymphoma
- Cryptococcus neoformans
- Coccidioidomyces immitis
- Toxoplasma gondii
- Pneumocystis jirovecii Answer D. Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease spread by eating raw or poorly cooked meat that contains cysts. It can also be acquired with exposure to animal feces (especially cats). In late stage AIDS patients can develop encephalitis and space occupying lesions. They may also develop necrotizing retinitis. It can be difficult to distinguish from primary CNS lymphoma. However, the patient in this question has cats which suggested Toxoplasma gondii as the causative organism. One way to distinguish this disease from other HIV related conditions is to treat for toxoplasmosis for three weeks and if improvement is seen then assume that is the diagnosis and continue treatment. If the condition does not improve, consider a brain biopsy.
AIDs and opportunistic infections.
- [PART 1 of 2] Growth hormone insensitivity in a group of extremely rare genetic disorders in which the body in unable to use the GH that it produces. Laron syndrome, for example, is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by insensitivity to GH, usually caused by a mutant GH receptor. Therefore, there is a failure of IGF-1 secretion in response to GH. Which of the following drugs would be most appropriate to treat this disorder?
- Somatotropin
- Mecasermin
- Octreotide
- Cosyntropin
- Pegvisomant Answer B. Mecasermin is synthetic IGF-1 and should be used in situations where children are insensitive to GH.
Endocrine Pharmacology.
- [PART 2 of 2] Which of the following is a likely side effect from this drug?
- Hyperglycemia
- Hypoglycemia
- Thrombosis
- Acute renal failure
- Hot flashes Answer B. Somatotropin is associated with hyperglycemia, while IGF-1 (Mecasermin) is associated with hypoglycemia.
Endocrine Pharmacology.
- Which of the following drugs is used to treat ITP (Immune thrombocytopenic purpura)?
- Somatotropin
- Mecasermin
- Octreotide
- Cosyntropin
- Pegvisomant Answer C. Octreotide is a somatostatin analog and is used in the treatment of ITP due to its ability to reestablish immune regulatory systems.
Endocrine Pharmacology.
- Which of the following drugs can be used in the treatment of hyperprolactinemia?
- Mecasermin
- Pegvismant
- Cabergoline
- Leuprolide
- NafarelinAnswer C. Cabergoline is a D2 agonist. Dopamine works to inhibit PRL. Bromocriptine also has the same MOA.
Endocrine Pharmacology.
- GnRH agonists are sometimes utilized in the treatment of infertility, but are much more often used in the suppression of gonadotropin release. Which of the following is a GnRH agonist?
- Ganirelix
- Cabergoline
- Pegvisomant
- Leuprolide
- Conivaptan Answer D. Most GnRH agonists have the suffix “-relin.” Leuprolide is the only exception. Remember that Leuprolide is “pro” luteinizing hormone
Endocrine Pharmacology.
- Which of the following is utilized in the treatment of hypervolemic hyponatremia?
- Conivaptan
- Desmopressin
- Pitocin
- Ganirelix
- Pegvisomant Answer A. Conivaptan (Vasopressin antagonist) blocks ADH receptors, causing diuresis without electrolyte loss. It can also be used to treat SIADH.
Endocrine Pharmacology.
- Prostate cancer can be treated with which of the following drugs?
- Fluoxymesterone
- Testosterona enanthate
- Tamoxifen
- Flutamide
- Methyltestosterone Answer D. Flutamide is an anti-androgen that is utilized in the treatment of metastatic prostate cancer.
Endocrine Pharmacology.
- Which of the following are secreted from the posterior pituitary?
- Oxytocin
- ADH
- PRL
- A & B
- A & C Answer D.
Endocrine Pharmacology.
- Adrenalectomy is an operation that removes one or both of the adrenal glands. In some cases, this is a necessary procedure to treat Cushing’s Disease. When this procedure has been performed, it can cause something called Nelson Syndrome. Which of the following would be a side effect of this condition?
- Bitemporal hemianopsia
- Hyperprolactinemia
- Infertility
- Acromegaly
- Hyperthyroidism Answer A. Mass effect is a common symptom with Nelson syndrome and can lead to bitemporal hemianopsia.
Hyper/Hypopituitarism.
- What is the most common type of pituitary adenoma?
- Somatotroph adenoma
- Corticotroph adenoma
- Lactotroph adenoma
- Gonadotroph adenoma
- Thyrotroph adenoma Answer C.
Hyper/Hypopituitarism.
- A 42 year old male patient presents with with weight gain, high blood pressure, hyperglycemia, and fatigue. The patient is also experiencing centripetal obesity and a buffalo hump. Labs show and elevation in cortisol. You perform a dexamethasone suppression test, which doesn’t seem to affect the cortisol levels. Which of the following is most likely responsible for the patients symptoms?
- Cushing’s Disease
- Pituitary Adenoma
- Pheochromocytoma
- Addison’s Disease
- Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis Answer B. This patient has cushing’s syndrome from a corticotroph adenoma secreting excessive ACTH. The Dexamethasone test was negative indicating that the symptoms are secondary (either due to an adenoma, or ectopic ACTH production).
Hyper/Hypopituitarism.
- A pathologist sends you back the analysis of a hypothalamic suprasellar tumor, but neglects to say the diagnosis. The tumor is described as a “discrete, encapsulated mass” which is “not densely adherent to adjacent brain.” A mutation in which of the following is most likely associated with this tumor?
- BRAF V600E
- CDKN1B
- Cyclin D1
- HRAS
- CTNNB1 Answer A. This patient most likely has a papillary craniopharyngioma. 95% are associated with mutations in BRAF V600E. Adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma would be described as having a palisading squamous epithelium, with adherence to adjacent brain. They often have fibrosis, inflammation, and are cystic with “machine oil” cyst fluid. Adamantinmous craniopharyngiomas are associated with mutations in WNT gene (CTNNB1) which encodes β-catenin.
Hyper/Hypopituitarism.
- A 17 year old female presents to you clinic and states that she is scared she might be pregnant after having intercourse with her boyfriend the previous night. She is asking for an emergency contraceptive. Which medication would be most appropriate to prescribe?
- Progesterone
- Norethindrone
- Norgestimate
- Mifepristone
- Exemestane Answer D. Mifepristone is a progesterone antagonist that is often used for postcoidal contraception. Ulipristal is also used for this purpose.
Gonadal Hormones.
- A 30 year old female presents to the clinic complaining of LBP following attempting a heavy deadlift at the gym. After imaging and a physical, you decide that her muscle is only strained. You prescribe NSAIDs. If the patient has a history of stomach ulcers, which of the following drugs would be beneficial to also prescribe?
- Mifepristone
- Dinoprostone
- Misoprostol
- Latanoprost
- Ulipristal Answer C. Misoprostol (PGE-1) plays a protective role on stomach mucosa.
Gonadal Hormones.
- The use of St John’s Wort can cause subtherapeutic levels of all except which of the following drugs?
- Theophylline
- Sertraline
- Digoxin
- Cyclosporin
- Warfarin Answer B. Sertraline is an SSRI, which is not associated with subtherapeutic levels with concurrent use of St John’s Wort. The use of antidepressants and stimulants with St John’s Wort should be used cautiously due to risk of serotonin syndrome. Drugs that can result in subtherapeutic levels with use of St John’s Wort includes Warfarin, HIV Drugs (PI/NNRTIs), Anticonvulsants, Theophylline, Birth control, Digoxin, Irinotecan, and Cyclosporin.
Vitamins.
- Which of the following is associated with vitamin A deficiency?
- Skin xerosis
- Alopecia
- Bone loss
- Nyctalopia
- Neonatal Hemorrhage Answer D. Nyctalopia (night blindness) is a result of Vitamin A deficiency. Skin xerosis, Alopecia, and bone loss are the results of Vitamin A excess. Neonatal hemorrhage can occur with vitamin K deficiency.
Vitamins.
- A 27 year old presents to the clinic for a woman’s wellness visit. She explains that her and her husband are wanting to conceive. Her husband was born with spina bifida and she is concerned about neural tube defects for their future children. She asks you how long and at what dose she should be taking folate before trying to conceive. What should you tell her?
- 2 months, 4mg/day
- 2 months, 1mg/day
- 1 month, 4 mg/day
- 1 month, 1 mg/day
- 6 months, 1 mg/dayAnswer C. Prenatal vitamins should be taken at least 1 month prior to attempting conception to prevent neural tube defects. Supplementation should be continued for the first 2-3 months of pregnancy.
- A 46 year old male patient presents to the clinic for a wellness exam. She has a BGL of 220 and you diagnose her with Type II diabetes. You counsel her on the appropriate diet and necessity of exercise in addition to prescribing Metformin. Which of the following vitamins are you going to also encourage the patient to take?
- Vitamin B6
- Vitamin B3
- Vitamin B1
- Vitamin B12
- Vitamin CAnswer D.
Vitamins.
- All of the following should be supplemented when prescribing proton pump inhibitors EXCEPT which?
- Fe
- Mg2+
- Ca2+
- B12
- K+ Answer E.
Vitamins.
- Which of the following drugs should be utilized for mercury poisoning?
- Succimer
- Penicillamine
- Deferasirox
- Dimercaprol
- EDTA Answer D.
Toxicology.
- A 22 year old female presents to the clinic with cystic acne that has yet to completely resolve with conventional antibiotics. You decide to add Isotretinoin to her treatment regimen. Which of the following should be your next course of action before allowing her to take this medication?
- Pregnancy test
- Ultrasound
- Add an iron supplement
- Test TSH
- Ask about herbal supplementsAnswer A. Isotretinoin is a vitamin A supplement that is teratogenic (associated with cleft palate and cardiac abnormalities). A pregnancy test should be done before starting a patient on this medication.
Vitamins.
- A 32 year old pregnant female presents 41 weeks term. You decide to induce her due to the risks associated with post-term labor utilizing IV oxytocin. High doses of oxytocin can be associated with which of the following?
- Hyponatremia
- Hyperpigmentation
- Weight Gain
- Decreased bone density
- Thrombosis Answer A. Oxytocin can cause activation of vasopressin receptors in high amounts, leading to hypervolemia and hyponatremia.
Drugs to Treat late stage pregnancy.
- A 32 year old male presents with a diffuse goiter of which the patient noticed a week prior. Patient is complaining of fatigue and weight gain. Dexamethasone suppression and cosyntropin tests were normal. Labs show elevated TSH and low T3/T4. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis of this patient?
- TSH secreting adenoma
- Graves Disease
- Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
- Non-functional pituitary adenoma
- Iodine deficiency Answer C.
Hyper/Hypothyroidism.
- Thyrotoxicosis should be managed with all EXCEPT which of the following?
- Beta Blockers
- NSAIDs
- Cholestyramine
- Radioiodine
- Levothyroxine Answer E.
Drugs to treat Thyroid Disorders.
- A 23 year old female patient with thyrotoxicosis and a history of asthma presents to the clinic. The patient is experiencing weight loss, insensitivity to heat, and tachycardia. You decide to treat with Methimazole (the patient denies pregnancy), NSAIDs, and Cholestyramine. Which of the following drugs would be most appropriate in treating the patients high heart rate?
- Diltiazem
- PTU
- Levothyroxine
- Propranolol
- Amiodarone Answer A. Beta blockers are contraindicated in this patient due to history of asthma. Diltiazem (a calcium channel blocker) should be utilized instead.
Drugs to treat Thyroid Disorders.
- Which of the following drugs is most appropriate to treat a pregnant patient (first trimester) with hyperthyroidism?
- Methimazole
- Propylthiouracil
- Carbimazole
- Levothyroxine
- Dessicated thyroid Answer B.
Drugs to treat Thyroid Disorders.
- A patient presents with symptoms of cortisol excess including striae, moon facies, and a dorsal fat pad. The patient denies any use of exogenous corticosteroids. Dexamethasone suppression test reveals that cortisol is decreased in response to high dose dexamethasone. Which of the following should be performed to distinguish between a pituitary and ectopic ACTH suppression?
- Inferior petrosal sinus sampling
- Cosyntropin response test
- TSH response test
- Ultrasound
- Fine needle aspiration of pituitary Answer A.
Adrenal Disorders.
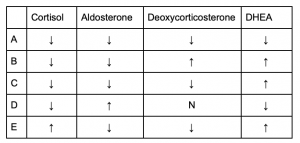
- [PART 1 of 3] Which of the following correctly describes the lab values of a patient with a 21 hydroxylase deficiency?

- A
- B
- C
- D
- EAnswer C.
Adrenal Disorders.
- [PART 2 of 3] Which of the following correctly describes the lab values of a patient with a 17 hydroxylase deficiency?

- A
- B
- C
- D
- EAnswer D.
Adrenal Disorders.
- [PART 3 of 3] Which of the following correctly describes the lab values of a patient with a 11β hydroxylase deficiency?

- A
- B
- C
- D
- EAnswer B.
Adrenal Disorders.
- A patient presents with moon facies, buffalo hump, diarrhea, and hypokalemia indicative of dehydration. Labs show elevated calcitonin. Calcium levels are 8.8 mg/dL (Normal 8.6-10.3 mg/dL). Patients vitals are all within normal range. Physical examination reveals a solitary thyroid nodule and FNA is ordered. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- Papillary Thyroid carcinoma
- Medullary Thyroid carcinoma
- Pheochromocytoma
- Anaplastic Thyroid carcinoma
- MEN Type 1Answer B. The solitary thyroid nodules indicates thyroid carcinoma. This patient is experiencing symptoms from ectopic ACTH and VIP secretion. This along with elevated calcitonin levels points to medullary thyroid carcinoma.
Primary endocrine carcinoma.
- Which of the following is a likely presentation with someone with MEN Type I?
- Hypertension
- Gastric ulcers
- Elevated calcitonin
- Marfan like habitus
- Hypocalcemia Answer B. MEN Type I is associated with the “three P’s” — Pituitary adenomas (GH, PRL usually), Pancreatic tumors (Insulinoma, gastrinoma), and Parathyroid tumors (increased parathyroid and subsequent hypercalcemia). Therefore, symptoms associated with this disease could include Zollinger-Ellison Disease (ulcers caused by gastrinoma), hypoglycemia (insulinoma), Acromegaly (GH secreting adenoma), Hyperprolactinemia (PRL-secreting adenoma), etc.
Primary endocrine carcinoma.
- Which of the following is a likely presentation with someone with MEN Type 2A?
- Hypoglycemia
- Gastric ulcers
- Neuromas
- Hypertension
- Acromegaly Answer D. MEN Type 2A is associated with Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma, Pheochromocytoma, and Parathyroid tumors. Therefore, presentation could include elevated calcitonin, hypertension, tachycardia, VMA in the urine, hypercalcemia, etc. Also note that medullary thyroid carcinoma is often associated with paraneoplastic syndromes due to ectopic ACTH/VIP which can lead to symptoms of dehydration (hypokalemia) and cushing’s disease.
Primary endocrine carcinoma.
- Which of the following is a likely presentation with someone with MEN Type 2B?
- Hypoglycemia
- Gastric ulcers
- Hyperextensibility of joints
- Acromegaly
- Hypercalcemia Answer C. MEN Type 2B is associated with Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma, Pheochromocytoma, Neuromas, and Marfan-like habitus. Therefore, presentation could include elevated calcitonin, ectopic ACTH/VIP secretion, hypertension, tachycardia, VMA in the urine, hyperextensibility of joints, etc.
Primary endocrine carcinoma.
- A 42 year old female patient presents with hypercalcemia, the cause of which is determined to be a parathyroid adenoma producing excess PTH. Upon further examination, the patient has multiple other endocrine neoplasms including a lactotroph adenoma. Genetic testing reveals an inactivating mutation in MEN1 tumor suppressing gene. Which of the following is this patient also likely to presenting with?
- Peptic ulcers
- Pheochromocytoma
- Medullary Thyroid carcinoma
- Hyperextensibility of joints
- Neuroma Answer A. This patient has Type 1 MEN, which usually presents with parathyroid hyperplasia/adenomas, pituitary adenomas, and pancreatic tumors (usually gastrinomas that result in peptic/gastric ulcers due to low pH).
Primary endocrine carcinoma.
- Which of the following would be a likely presentation for a patient with a glucagonoma?
- Hypoglycemia
- Peptic ulcers
- Hypertension
- Hypokalemia
- Migratory necrolytic erythema Answer E.
Primary endocrine carcinoma.
- 25 year old female patient presents with skin lesions and diarrhea. Patient was put on Nacin (B3) supplements by her primary care physician 2 months prior, but symptoms have yet to subside. Labs reveal elevated 5-HT. Which of the following is a likely diagnosis?
- Carcinoid
- Insulinoma
- Glucagonoma
- Pheochromocytoma
- Pellagra Answer A.
- Which of the following is highly associated with Type II Diabetes?
- Amyloid deposition
- Autoimmune destruction of β-cells
- DKA
- HLA-DR-3
- Weight loss Answer A.
- Which is the first line of treatment for Type II Diabetes Mellitus in conjunction with diet and exercise?
- Acarbose
- Glyburide
- Metformin
- NPH
- Sitagliptin Answer C.
Drugs to treat Disorders of the Pancreas.
- [PART 1 of 2] A 52 year old male patient presents to the clinic requesting a change in medication. He was previously diagnosed with Type II Diabetes and was prescribed Metformin. He is complaining that this medication is causing nausea and diarrhea which inhibits his day to day function. The patient has a BMI of 35%. The patient also has a history of CHF. Which of the following drugs would be most appropriate to prescribe this patient?
- Exenatide
- Glyburide
- Sitagliptin
- Pioglitazone
- Acarbose Answer C. Sitagliptin is the only medication that is appropriate for treating a Type 2 DM patient that is not contraindicated. Answer A and E are associated with GI symptoms that the patient is trying to avoid. Answer D is contraindicated in patients with CHF (black box warning!!). Lastly, answer B is incorrect because it is contraindicated in obese patients.
Drugs to treat Disorders of the Pancreas.
- [PART 2 of 2] What is the mechanism of action for the drug chosen in part 1 of this question?
- Increases insulin sensitivity
- Incretin analog
- Inhibits PPAR𝝲
- Inhibits ATP-dependent K+ channels
- Inhibits DPP-4 Answer E. Sitagliptin works by inhibiting DPP-4, effectively increasing the ½ life of incretin.
Drugs to treat Disorders of the Pancreas.
- A 34 year old woman reports to your office for a well woman exam. The patient history is significant for menarchy at age 12, coitarchy at age 14, and a history of multiple sexual partners. She is complaining that lately she sometimes has postcoital spotting. Exam shows no cervical discharge, and Pap smear reveals the presents of koilocytes. Which of the following agents is likely causing the patient’s symptoms?
- Chlamydia trachomatis
- Treponema pallidum
- Trichomonas vaginalis
- HPV
- HSVAnswer D. Koilocytes are pathomnemonic for HPV infections.
- A 58 year old woman comes to your clinic complaining of breast tenderness. She is concerned that she may have breast cancer, as her mother and grandmother did. History reveals newly onset vaginal bleeding, although her last menstruation was 3 years ago. On physical exam, you are able to palpate a unilateral adnexal mass. Endometrial biopsy shows signs of hyperplasia. The likely cause of these findings would be which of the following?
- Adverse drug effect
- Granulosa cell tumor
- Endometrial carcinoma
- Leiomyosarcoma
- FibromaAnswer B. Granulosa cell tumors secrete unopposed estrogen, causing breast tenderness, endometrial hyperplasia, and postmenopausal bleeding.
- A 17 year old female patient complaining of general abdominal discomfort and difficulty tolerating heat is revealed to have a firm adnexal mass on physical exam and labs return with elevated hCG and LH.
A surgical consult results in the ultimate removal of an ovarian mass. Pathology shows the exhibit below. What was the final diagnosis for this patient?
- Dysgerminoma
- Yolk Sac Tumor
- Embryonal Tumor
- Choriocarcinoma
- Endodermal sinus tumor Answer A. This is the characteristic “fried egg” appearance of dysgerminoma.
- A 23 year old female presents to your office complaining of irregular menstruation hoping to get help regulating her periods. Physical exam reveals a well developed female of seemingly good health with a BMI of 21, with coarse hair above the upper lip and on the chest. Vital signs show a HR of 72 and BP of 145/86 with a temperature of 98F. Which of the following would be the most likely adrenal enzyme deficiency in this patient, were she to have one?
- 17α-Hydroxylase
- 21-Hydroxylase
- 11β-Hydroxylase
- 3β-HSD
- AromataseAnswer C. Virilization of the female with high blood pressure should indicate a deficiency of 11B-hydroxylase.
- Which of the following would directly cause an increase in secretion of PTH?
- Increased serum calcium
- Decreased serum phosphate
- Low serum magnesium
- Increased serum potassium
- Decreased serum sodiumAnswer C. While severe loss of magnesium due to diarrhea, aminoglycosides, diuretics, or alcohol abuse can cause PTH to decrease, moderately low serum magnesium will increase PTH secretion. Choices A and B are the opposite case of what is correct. Potassium and sodium have no direct impact on PTH levels.
- Elevated appetite, blood pressure, and gluconeogenesis with marked eosinopenia could indicate a functional lesion in which area?
- Adrenal zona glomerulosa
- Adrenal zona fasiciculata
- Adrenal zona reticularis
- Adrenal medulla
- Posterior pituitary gland Answer B. These symptoms would be indicative of hypersecretion of cortisol, which is made in the zona fasiculata of the adrenal cortex.